 |
| Acid and properties - class X notes |
What is an Acid ? it is most important topic of NCERT Acid , base and Salt chapter 2 in Class 10th. Questions are frequently asked in the CBSE board and ICSE Board exam from Acid .
“Chemistry – Acid class 10 notes “ will be very beneficial for the
students who are engaged in the preparation of
upcoming board exam.
In this topic, the following terms will be
illustrated.
Contents :
* What is and Acid
* Physical properties of acids
* Types of acid : Organic acid, Inorganic acid, Strong acid,
Weak acid, Dilute acid , Concentrated Acid
* Chemical Properties of Acids : Chemical
Reactions
* Preparation of acids
* Uses of acids
* Fire extinguisher , Acid Rain, Dilution of acid
What is and Acid
- According to Arrhenius , Those substances which dissociate into hydrogen ions ( H+ ) in aqueous solution are called acids.
- Hydrogen ion ( H+ ) is too reactive. It react with water molecule to form hydronium ion ( H3O+) .
- i.e. acids are the substance which produce hydronium ions ( H3O+) in aqueous solution . e.g. HCl, H2SO4 , CH3COOH, etc
Poperties of Acids:
- The term acid has been derived from the latin word ‘acidus’ which means sour. i.e acids are sour in taste.
- It turns blue litmus red.
- It destroys body tissue.
- It corrode metal surface.
- It react with metal to produce hydrogen gas.
1. On the basis of origin:
- It is derived from living organism like plants and animals.
Organic acid | sources |
Citric acid | Fruits |
Acetic acid | Vinegar |
Oxalic acis | Tomato |
Tartaric acid | Tarmind |
Lactic acid | Milk, Curd |
Formic acid | Antsting, Nettle sting |
Ascorbic acid | Guava, Amla |
- Its molecules consists carbon atom along with hydrogen and other atoms
- It is a weak acid.
- It is derived from minerals, so it is also called mineral acid. e.g HCl, H2SO4 etc.
- Its molecule does not contain carbon atom except carbonic acid ( H2CO3 ).
- It is strong acid except carbonic acid ( H2CO3 ).
Common Name of Inorganic Acid
* H2SO4
- Oil of vitriol
* HCl - Muriatic acid
* HNO3 - Aqua
fortis ,
spirit of niter
- An acid which completely dissociates into ions is called strong acid.
- Its each molecule dissociates into Hydrogen ions.
- Inorganic acids are strong acid except carbonic acid (H2CO3 ) .
- An acid which does not completely dissociates into ions is called weak acid.
- Its few molecule dissociates into ions.
- Organic acids are weak acid .
- If amount of hydrogen ions ( H + ) are very low in per unit volume of solution, then acid is said to be dilute acid.
- i.e in dilute acid , amount of water is very large than amount of acid.
- If amount of hydrogen ions ( H + ) are large in per unit volume of solution, then acid is said to be concentrated acid.
- i.e in concentrated acid , amount of water is less than amount of acid.
- Acids are sour in taste.
- Some acids are solid and some are liquid at room temperature.
Solid Acids | Boric acid ( H3BO3 ) Oxalic acid ( COOH )2 Tartaric acid( C4H6O6 ) Citric acid ( C6H8O7 ) Phosphoric acid ( H3PO4 ) |
Liquid acid | Acetic acid - ( CH3COOH ) Formic acid - ( HCOOH ) Carbonic acid- (H2CO3 ) Hydrochloric acid - HCl Sulphuric acid - H2SO4 Nitric acid - HNO3 etc. |
- All minerals acid except carbonic acid are harmful for skin . it destroys body tissue.
- Organic acid and carbonic acid do not effect on skin.
- Inorganic acid corrode metal surface.
- Organic acid and carbonic acid are not corrosive.
- Aqueous solution of acid are good conductor of electricity due to formation of ions.
- Acid change color of some indicators.
Indicator | Color changed |
Litmus | Blue to red |
Methyl orange | Orange to pink |
Acid + | Reactant = | Product |
Dilute ( HCl or H2SO4 ) | Metal | Salt + H2 |
Metal oxide | Salt + H2O | |
Alkali | Salt + H2O | |
Metal carbonate | Salt + CO2 + H2O | |
Metal bi-carbonate | Salt + CO2 + H2O | |
Metal sulphite | Salt + SO2 + H2O | |
Metal bi-sulphite | Salt + SO2 + H2O | |
Metal sulphide | Salt + H2S | |
Pb(NO3)2 | Salt + HNO3 | |
Concentrated (H2SO4) | Metal Chloride Metal Nitrate | Salt + HCl Salt + HNO3 |
- Acid react with metal to form metal salt and hydrogen gas.
- (a) Dilute HCl and H2SO4 react explosively with active metal like K, Na, Ca .
- (b) Dilute HCl and H2SO4 react moderately with less active metal like Mg, Zn, Fe.
- (c) HNO3 is not used for this reaction because of it is very strong oxidizing agent which oxidize hydrogen into water.
- Only magnesium (Mg) and manganese (Mn) produce hydrogen gas with very dilute nitric acid ( 1%).
- Acid react with base to form salt and water only. This reaction is called neutralization reaction.
Strong acid + Strong base → Neutral salt + H2O Strong acid + Weak base → Acidic salt + H2O Weak acid + Strong base → Basic salt + H2O Weak acid + Weak base → Neutral salt + H2O |
- Only nitrate of lead metal react with dilute HCl or H2SO4 .
- Other metal nitrate react with concentrated H2SO4 on heating.
- Metal chloride react only with concentrated H2SO4 on heating.
- Binary acids ( acid containing two atoms ) are prepared by this method.
- NO2 gives two acid , so it is called double acid anhydride.
- Metal chloride react with concentrated H2SO4 on heating to produce hydrochloric acid .
- Only nitrate of lead metal react with dilute HCl or H2SO4 to produce nitric acid .
- Other metal nitrate react with concentrated H2SO4 on heating to produce nitric acid .
Acid | Uses in |
Acetic acid | Vinegar and cooking |
Boric acid | Eyewash and antiseptic |
Benzoic acid | Preservation of food Making of perfume and medicine |
Citric acid | Food preservation Preparation of vitamine C |
Carbonic acid | Use in soft drink |
Hydrochloric acid | Cleaning of metal item |
Nitric acid | Making explosive |
Oxalic acid | Ink stain remover |
Phosphoric acid | Fertilizers |
Tartaric acid | Baking powder |
- Mixture of 3 part of conc. Hydrochloric acid and 1 part of Conc. Nitric acid is called aqua regia .
- It dissolves all metals even nobel metal like platinum and gold etc.
- It is a device used in putting off fire .
- Metal carbonate or bicarbonate and acid are used in fire extinguisher to produce CO2 gas.
- Acid and carbonate are kept in separate chamber in fire extinguisher.
- On emergency , they are allowed to react with each other to form CO2 gas.
- As carbon dioxide does not support burning, it put off the fire.
- It is tested by burning a lighted candle near it.
- If the gas burns with pop sound , then it confirm that the evolution of hydrogen gas.
- Burning with pop sound is the characteristics test for hydrogen gas.
- Rain containing nitric acid and sulfuric acid is called acid rain.
- When pH of rain water is less than 5.6, it is called
acid rain.
- When acid rain flows into the rivers, it lowers the pH
of the river water. The survival of aquatic life in such rivers becomes
difficult.
- Burning of fossil fuels release oxides of sulphur and nitrogen.
- NO2 and SO2 form nitric acid and sulfuric acid on reaction with water of rain droplets.
- Acid rain causes damage to the trees , historical monuments and other building.
- Tajmahal which is made of marble is getting damage due to acid rain. Marble is calcium carbonate ( CaCO3 ) which react with acid and thus get corrode.
 |
|
- The process of dissolving an acid or a base in water is highly exothermic.
- If water is added to acid, the heat generated may cause the mixture splash out and glass container may also break due to excessive heating.
 |
| Tartaric acid |
 |
| Lactic acid |
 |
| Ascorbic acid |
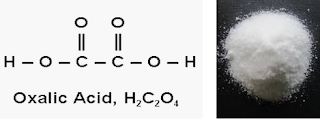 |
| Oxalic acid |
 |
| Malic acid |
 |
| Citric acid |
If you liked the notes of What are acids - Chemical properties, then share it with other students.
If you want to ask any question related to topic Chemistry – Acid class 10 notes then write question in the comment box.
Related Article ( Must read )
* Base and Alkali – Chemistry Notes Class 10
* Define Indicator in Chemistry –Notes Class 10
* What is Salt – Chemistry Notes Class 10
* Acid Base Salt - common name



No comments:
Post a Comment