What is magnetic field class 12 ? CBSE Notes Class 12 Physics Magnetism
is most important topic of NCERT Magnetic
effect of electric current chapter in Class 12.
Questions are frequently asked in the CBSE board , ICSE Board and other competitive exam ( IIT
JEE, NEET, AIIMS, State Engineering exam
) from
Magnetic Field - CBSE NCERT Notes Class 12 Physics .
“magnet and magnetism class 12 notes “ will be very beneficial for
the students who are engaged in the preparation of upcoming board exam.
In this topic,
the following terms will be illustrated.
Contents :
* 1. Magnet : Natural Magnet ( Permanent Magnet ), Electromagnet, Bar
magnet, Horseshoe magnet, Uses Of
Magnet,
* 2. MAGNETIC FIELD: Magnetic Field Lines, Properties of Magnetic Lines of Force,
* 3. Uniform magnetic field, Non-uniform magnetic field
* 4. Modern view about magnetism
* 5. Magnetic flux (ϕ ), MAGNETIC FLUX DENSITY ( B )
* 6. Coulomb's law of force for magnetic poles
What is Magnet
A substance that attract pieces of iron, steel and cobalt is called a magnet and this property of magnet
is called magnetism.
Magnets come in various shapes and sizes depending on
their intended use. Two of the most common magnets are the bar magnet and Horseshoe magnet .
On the basis of formation , these are two types :
1. Natural Magnet ( Permanent Magnet ) :
* Natural magnet is
iron oxide ( Fe2O3 ) which is found in nature as black stone.
* Natural magnet is not so important in electrical field because of its low magnetic strength.
2. Electromagnet :
* Magnet formed by passing electric current through a
wire wound over magnetic material like iron, steel etc is called electromagnet .
* It is a temporary magnet because when current is stopped
then magnetism is vanished.
* The main advantage of an electromagnet is that it can be
made of desired strength and shape.
Bar magnet:
 |
| Field pattern in bar type magnet |
* A bar magnet is a long, rectangular bar of uniform cross-section which attracts pieces of iron, steel, nickel and cobalt. . This type of magnet can be either a permanent magnet or an electromagnet.
* The attraction is maximum at the ends of bar magnet and least at the middle.
* The two ends of bar magnet where magnetic strength is maximum are called poles of the magnet. A magnet has two poles : North pole and South pole
* Like pole repel each other and unlike pole attract each
other.
* A freely suspended bar magnet always stay in north- south direction. The end of magnet toward North direction is called North pole and the end toward South direction is called South pole.
* The pole of magnet can not be separated . If a bar magnet is
broken into many parts then each part behave as a magnet and consists two poles
. ie an isolated magnetic pole does not exist.
* Both pole of magnets
have equal strength.
The pole strength is represented by m. the S.I unit of pole strength is Ampere meter
( Am ) or Weber
* The distance between two pole of magnet is called magnetic
length.
It is slightly less than the geometrical length of the
magnet.
 |
| Ie. Magnetic length = 6/7 Geometrical length. |
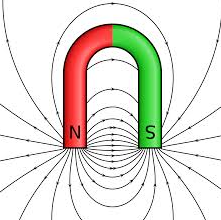
Horseshoe magnet
* A horseshoe magnet is made in the shape of a horseshoe or a U shape .
* A horseshoe magnet is stronger because both poles of the magnet are closer to each other .
* So , It create a much stronger magnetic field between the
poles . This is main advantage of a
horseshoe magnet over other types of magnets .
* This type of magnet can be either a permanent magnet or an electromagnet.
Field pattern in horseshoe magnet :
Uses Of Magnet :
* Magnets are used for a variety of purposes.
* Magnets are used in radio, television, and stereo
speakers.
* Magnets are used in refrigerator doors, in audio and
video cassette tapes.
* Magnets are used in hard discs and floppies for computers, and in children's toys.
* Magnets are used in motors , Alternator.
* The Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MK) technique which is
used to scan inner human body parts in hospitals also uses magnets .
* Magnets are used
for making electric generators and electric motor.
MAGNETIC FIELD
The space in which a magnetic pole or magnetic material like iron,steel ,
cobalt experiences a force is called a magnetic
field.
i.e Magnetic field exists around a magnet. If an
isolated magnetic pole is brought near a magnet, it experiences a force .
Magnetic Field Lines:
* The curve drawn around the magnet along which a
hypothetical north or south pole move is called Magnetic Field Line.
* The magnetic field lines are also known as magnetic
lines of force. It is vector quantity.
Properties of Magnetic Lines of Force
(i) Magnetic
lines of force emerge from n-pole of the
magnet, pass through the surrounding medium and re-enter the s-pole.
* Inside the magnet, each magnetic line of force passes from s-pole to n-pole. Thus Each magnetic line of force forms a closed loop
(ii)The magnetic field is strongest near the pole of magnet and goes on decreasing in strength as we move away from the magnet.
(ii) The
direction of magnetic flux density (B) at a point is that of the tangent to the
magnetic field line at that point.
(iii) No two magnetic lines of force can intersect
each other.
* If two magnetic lines
of force intersect, there would be two directions of magnetic field at that
point which is not possible.
(iv) Where the magnetic lines of force are close
together, the magnetic field is strong and where they are well spaced out, the
magnetic field is weak.
* i.e crowded magnetic lines of force means
stronger magnetic field and vice-versa.
(v) The larger
the number of magnetic field lines crossing per unit normal area, the larger is
the magnetic flux density (B).
(vi) Magnetic lines of force contract longitudinally
and widen laterally.
vii) Magnetic lines of force are always ready to pass
through iron or other magnetic material, in preference to passing through air,
even though their closed paths are made longer thereby.
UNIFORM AND NON-UNIFORM MAGNETIC FIELD
(i) Uniform magnetic field
The region in which magnitude and direction of
magnetic flux density at every point is constant is known as uniform magnetic
field.
For example, the earth's magnetic field is nearly
uniform. This means that magnitude and direction of magnetic flux density at
every point on earth's surface is nearly the same.
Representation of uniform magnetic
field
* A uniform magnetic field acting in the plane of the paper is
represented by parallel and equidistant magnetic lines of force .
* A uniform magnetic field acting
perpendicular to the plane of the paper and directed downwards is represented
by equally spaced crosses
* A uniform magnetic field acting perpendicular to the plane
of the paper and directed upwards is represented by equally spaced dots
(ii) Non-uniform magnetic field
The magnetic field in a region is non-uniform if the
magnitude or direction of magnetic flux density varies from point to point in
the region.
For example, the magnetic field due to a bar magnet is
non-uniform i.e. magnitude and direction of magnetic flux density varies from
point to point.
* A non-uniform
magnetic field is represented by converging or diverging magnetic lines of
force.
MODERN VIEW ABOUT MAGNETISM
According to modern view,
* An atom consists of central nucleus with electrons revolving
around the nucleus in different orbits. This motion of electrons is called
orbital motion
* The electrons also rotate around their own axis. This motion
of electrons is called spin motion
* Due to these two motions, each atom is equivalent to a
current loop i.e. each atom behaves as a magnetic dipole.
* Thus magnetic properties of a substance are attributed to
the motions of electrons (orbital and spin) in the atoms. Spinning motion of electrons in particular is
responsible for magnetism of a substance.
* In the unmagnetized substances, the magnetic dipoles are
randomly oriented so that magnetic fields mutually cancel.
* When the substance is magnetised, the magnetic dipoles are
aligned in the same direction. Hence the substance shows net magnetism.
* Since the revolving
and spinning electrons in each atom cause magnetism, no substance is
non-magnetic.
Magnetic flux (ϕ )
The amount of magnetic field produced by a magnetic
source is called magnetic flux. Magnetic flux is denoted by Greek letter ϕ .
e.g , If 10 magnetic lines come out of the north
pole a enter the south pole of a magnet, then magnetic flux , ϕ = 10 lines or Maxwell.
* The SI unit of magnets
flux is Weber.
* 1 Wb = 108
lines
MAGNETIC FLUX DENSITY ( B )
Amount of flux passing normally through unit area is called magnetic flux
density .
i.e Flux
density is a measure of field concentration .
* B = Flux / Area
* The SI unit of magnetic flux density is Wb/m2 or Tesla.
* Magnetic flux density is a vector quantity.










No comments:
Post a Comment