This article includes type of chemical reaction such as Combination reactions, Decomposition reactions, Displacement reactions, Double displacement reactions,Oxidation and Reduction reactions, Exothermic reaction, Endothermic reaction. we will also discuss precipitates and their colour and solubility in water.
respiration reaction , photosynthesis and rancidity of food item are explained well.
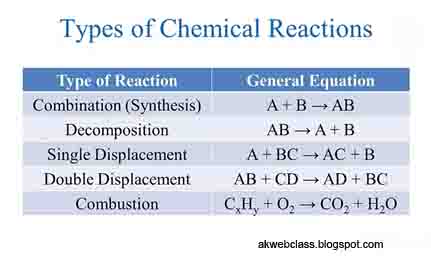 |
| Types of Chemical reaction |
TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS :
- Some of the important types of chemical reactions are :
1. Combination reactions,
2. Decomposition reactions,
3. Displacement reactions,
4. Double displacement reactions,
5. Oxidation and Reduction reactions.
6. Exothermic reaction
7. Endothermic reaction
COMBINATION REACTIONS :
- The reaction in which two or more substances combine to form a single substance, is called combination reactions.
Examples of combination reactions:
- CaO(s) + H2O (l) → Ca(OH)2 (s)
- 2SO2 (g) + O2 (g) → 2SO3 (g)
- 2H2 (g) + O2 (g) → H2O (l)
- C (s) + O2 (g) → CO2 (g)
- 4Na (s) + 2O2 (g) → 2Na2O (s)
- 2Na (s) + Cl2 (g) → 2NaCl (s)
Decomposition Reaction:
- The reaction in which a single compound split into two or more simpler substances is called decomposition reaction.
- Decomposition reaction occur in presence of heat or light or electricity.
- So there are three types of decomposition reaction.
(1) Thermal Decomposition Reaction:
- When decomposition reaction is occurred on heating , it is called thermal decomposition reaction.
For examples:
- CaCO3 (s) → CaO (s) + CO2 (g)
- 2KClO3 (s) → 2KCl (s) + 3O2 (g)
- 2 FeSO4 (s) → Fe2O3 (s) + SO2 (g) + SO3 (g)
- 2Pb(NO3) (s) → 2 PbO (s) + 4 NO2 (g) + O2 (g)
(2) Photolytic Decomposition Reaction:
- When decomposition reaction is occurred in presence of sun light ,it is called Photolytic decomposition reaction.
Example:
- When silver chloride is exposed to light, it decompose into silver metal and chlorine gas.
2 AgCl (s) → 2 Ag(s) + Cl2 (g)
This reaction is used in black and white photography.
- 2 AgBr (s) → 2 Ag(s) + Br2 (g)
(3) Electrolytic Decomposition Reaction:
- When decomposition reaction is occurred in presence of electricity ,it is called electrolytic decomposition reaction.
Example:
- 2 NaCl → 2 Na + Cl2
- 2 H2O (l) → 2H2 (g) + O2 (g)
(4) Displacement Reaction:
- The reaction in which an element displaces other element from its compound is called displacement reaction.
- In this reaction a more reactive element displace less reactive elements.
Examples:
- CuSO4 (aq) + Zn (s) → ZnSO4 (aq) + Cu(s)
- CuSO4 (aq) + Fe (s) → FeSO4 (aq) + Cu(s)
- CuCl2 (aq) + Pb(s) → PbCl2 (aq) + Cu(s)
- AgNO3(aq) + Cu(s) → Cu(NO3)2 (aq) + 2Ag(s)
(5) Double Displacement Reaction:
- The reaction in which two elements interchange their position from their respective compounds is called double displacement reaction.
Example:
- AgNO3 (aq) + NaCl (aq) → AgCl (s) + NaNO3 (aq)
- BaCl2 (aq) + Na2SO4 (aq) → BaSO4 (s) + 2NaCl (aq)
- BaCl2 (aq) + CuSO4 (aq) → BaSO4 (s) + CuCl2 (aq)
- CuSO4 (aq) + H2S (g) → CuS (s) + H2SO4 (aq)
- AlCl3 (aq) + 3NH4OH (aq) → Al(OH)3 (s) + 3NH4Cl (aq)
- Pb(NO3)2 (aq) + 2KI (aq) → PbI2 (s) + 2KNO3 (aq)
- A double displacement reaction usually occurs in solution.
- Generally one of the product is formed as a insoluble precipitate.
Some Common Precipitates and Their Colour:
Precipitate | colour |
AgCl | White |
BaSO4 | White |
Al(OH)3 | White |
PbCl2 | Colourless |
ZnSO4 | Colourless |
MgSO4 | Colourless |
AgNO3 | Colourless |
Pb(NO3)2 | Colourless |
CuCl2 | Green |
FeSO4 | Greenish |
PbI2 | Yellow |
PbO | Yellow |
CuSO4 | Blue |
Cu(NO3)2 | Blue |
CuS | Black |
Fe2O3 | Brown |
Solubility of some common precipitaes:
Soluble ppt. | Insoluble ppt. |
CuSO4 ,ZnSO4 , MgSO4 ,FeSO4, Na2SO4 , NaCl, KCl, CuCl2, PbCl2 , FeCl2 , MgCl2 , BaCl2 AgNO3, Cu(NO3)2 | BaSO4 AgCl, PbI2 CuS, Al(OH)3 |
(6) Oxidation Reaction and Reduction Reaction:
- In term of oxygen and hydrogen:
Oxidation:
- Addition of oxygen to a substance is called oxidation reaction.
- Removal of hydrogen from a substance is called oxidation reaction.
- That substance is oxidized and called reducing agent.
- e.g , C + O2 → CO2
Carbon is oxidized and acts as a reducing agent. Thus , reaction is oxidation reaction.
- CuO + H2 → Cu + H2O
Hydrogen is oxidized and acts as a reducing agent.
Reduction:
- Removal of oxygen from a substance is called reduction reaction.
- Addition of hydrogen to a substance is called reduction reaction.
- That substance is reduced and called oxidizing agent.
e.g ,
- CuO + H2 → Cu + H2O
Hydrogen is oxidized and acts as a reducing agent.
(7) Exothermic Reaction:
- The reaction in which heat is evolved is called exothermic reaction.
e.g
- Burning of coal, Burning of natural gas, Burning of magnesium ribbon, Burning of LPG, Respiration reaction etc.
- C + O2 → CO2 + Heat
- CH4 + 2O2 → 2H2O + CO2 + Heat
(8) Respiration Reaction:
- During digestion, starch carbohydrate is broken down into Glucose.
- Glucose reacts with oxygen in the cell of humane body to produce energy along with water and carbon dioxide gas. This reaction is called respiration reaction.
(9) Endothermic Reaction:
- The reaction in which energy is required to form products is called endothermic reaction.
e.g, Photosynthesis reaction
All decomposition reaction is endothermic reaction.
For example:
N2 (g) + O2 (g) + Heat energy → 2NO (g)
2 AgCl (s) + light energy → 2 Ag(s) + Cl2 (g)
2 NaCl + Electrical energy → 2 Na + Cl2
CaCO3 (s) + Heat → CaO (s) + CO2 (g)
KClO3 (s) + Heat → 2KCl (s) + 3O2 (g)
2 FeSO4 (s) + Heat → Fe2O3 (s) + SO2 (g) + SO3 (g)
2Pb(NO3) (s) + Heat → 2 PbO (s) + 4 NO2 (g) + O2 (g)
Photosynthesis :
- The reaction between carbon dioxide and water in presence of sunlight and chlorophyll of green plants is called photosynthesis.
- Photosynthesis is occurred in leaves of green plants.
- Since sunlight energy is required in photosynthesis , so it is an endothermic reaction.
In presence of chlorophyll,
- 6CO2 (g) + 6H2O (l) + Light → C6H12O6 (aq) + 6O2 (g)
Rancidity :
- When the fats and oils present in food materials get oxidized by the oxygen (of air), then oxidation products have unpleasant smell and taste. This process is called rancidity.
- The characteristics of a rancid food are that it gives out an unpleasant smell and also has an unpleasant taste.
- Rrancidity of food can be prevented by some methods:
(1) By Adding Anti-Oxidants:
- Rancidity can be prevented by adding anti-oxidants to foods .
- Anti-oxidants are reducing agents. The two common anti-oxidants used in foods to prevent the rancidity are BHA (ButylatedHydroxy-Anisole) and BHT (Butylated Hydroxy-Toluene).
 |
| BHA (ButylatedHydroxy-Anisole) |
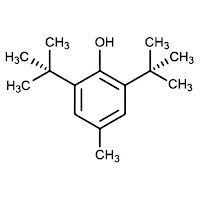 |
| BHT (Butylated Hydroxy-Toluene). |
- When antioxidants are added to foods, then the fats and oils present in them do not get oxidized easily and hence do not turn rancid.So the foods remain good to eat for a much longer time.
(2) By Nitrogen Gas:
- Rancidity can be prevented by packaging fat and oil-containing foods in nitrogen gas.
- When the packed food is surrounded by non reactive gas nitrogen, there is no oxygen to cause its oxidation and make it rancid.
(3) By Cooling :
- Rancidity can be retarded by keeping food in a refrigerator .
- The refrigerator has a low temperature inside it. When the food is kept in a refrigerator, the oxidation of fats and oils in it is slowed down due to low temperature. So, the development of rancidity due to oxidation is retarded.
(4) Storing Food in Air-Tight Containers.
- When food is stored in air-tight containers, then there is little exposure to the oxygen of the air. Due to reduced exposure to oxygen, the oxidation of fats and oils present in food is slowed down.

No comments:
Post a Comment