Magnetic effect of electric current is most important topic of NCERT Physics in Class 12 . Questions are frequently asked in the CBSE board , ICSE Board and other competitive exam from Current and magnetism .
“physics - Electric current and magnetism 12th notes “ will be very beneficial for the students who are engaged in the preparation of upcoming board exam .
In this topic, the following terms will be
illustrated.
* Magnetic effect of electric current
* Oersted Experiment
* Amperes swimming rule
* Magnetic field
* Magnetic flux density ( B )
* Magnetic Force on moving charge
* Biot-savart Law
* Biot-savart formula
in vector form
Magnetic effect of electric current :
Magnetic effect of electric current was discovered by
oersted in 1820.
According to Oersted , A current carrying conductor produces a magnetic field around it. In other words, electric current can produce magnetism. This Phenomenon is called 'magnetic effect of electric current.
He verified the magnetic effect of electric current by
the following simple experiment.
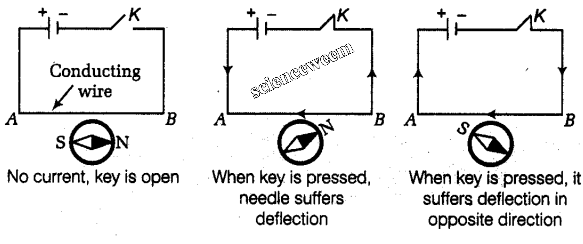
Oersted Experiment :
* Put a conducting wire AB above magnetic needle parallel to
it. When
no current flows in the wire then there is no deflection in the magnetic
needle and it remains parallel to the wire.
* As soon as the current flow through the wire AB the needle
is deflected . when the current in wire AB
is reversed, the needle is deflected in the opposite direction.
This experiment gives following result,
* This deflection is a convincing proof of the existence of
magnetic field around a current carrying conductor.
* On increasing the current in the wire AB , the deflection of
the needle is increased and vice versa. This
show the magnetic field strength increases with the increase in current and
vice versa.
* It is clear from Oersted experiment that current carrying conductor produces a magnetic field around it. The larger the value of current in the conductor the stronger is the magnetic field and vice versa.
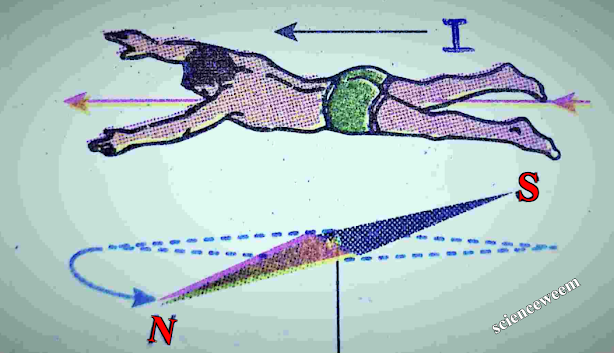
Amperes swimming rule :
The direction of deflection of the magnetic needle due
to current in the wire is given by Ampere swimming rule. It is state as
Imagine a man is swimming along the wire in the
direction of the flow of current . His face always turned toward the magnetic
needle so that the current enters through his feet and leaves at his head .
Then N -pole of the magnetic needle will be deflected toward his left hand.
Magnetic field :
The region
around magnet or a current carrying conductor where magnetic effect can
be experienced is called a magnetic
field.
* The magnetic field is represented by magnetic lines of
force, which form of closed loop.
* The greater the current through the
conductor the stronger is the magnetic field and vice versa.
* The magnetic field disappear as soon as the current is
Switched off or charge it stopped.
Magnetic Field Lines:
* The curve drawn around the magnet along which a hypothetical north or south pole move is called Magnetic Field Line.
* The magnetic field lines are also known as magnetic lines of force. It is vector quantity.
Magnetic flux density ( B )
* Magnetic flux density is a measure of field concentration.
* Magnetic flux density is also called magnetic field B̅ . and defined
as
Amount of
magnetic flux passing normally through unit
cross section area is called magnetic field .
Thus , magnetic field
= magnetic flux / area of cross section
* It is a vector quantity and is represented by a symbol B .
* Its S.I unit is wb/m2 or
Tesla or N/A-m
1 Tesla = 1 wb/m2
* CGS unit of magnetic
field is Gauss ( G ) .
1 Tesla = 104 G
Magnetic Force on moving charge :
Magnetic field exert a force on moving charge. This
force depends on following four factors
* Magnitude of charge : Fm
∝ q
* magnetic field density : Fm ∝ B
* speed of charge :
Fm ∝ v
* Angle between direction of motion of positive charge and direction of magnetic field.
Fm ∝ sin θ
Combining all factors,
We get , Fm ∝ qBv sin θ
Fm = k
qBv sin θ
From
experiments value of k = 1
So, Fm = qBv sin θ
Vector form : Fm = q (v x B )
Direction of magnetic force on charge is
always perpendicular to plane containing v and B vectors .
Define Magnetic field in term of magnetic force :
Fm = qBv sin θ
If q = 1 C, v = 1m/s2 and θ
= 900
Then ,
Fm = B
* Thus, When
unit charge move perpendicular to magnetic field with unit speed at any point . Then magnetic field at that point is equal
to force acting on charge .
Biot-savart Law :
Biot-savart conducted several experiments to study the
magnetic field produced by current carrying conductors.
On the basis of experiments they concluded that the
value of the magnetic field produced
by a current carrying small segment conductor
at any point depends on the following
four factors.
* dB ∝ I
* dB ∝ dl
* dB ∝ sin θ
* dB ∝ 1 / r2
Combining all four factors, we get
or,
where
K is magnetic constant . Its value depends on the medium in which the
conductor is situated .
where , K
= μ / 4 π and
So , For any medium ,
* μ = Absolute permeability of medium
* μ0 =
Absolute permeability
of free space and μ0 = 4 π
x 10-7 Tm / A or N / A
* μr =
Relative permeability of medium
* for free space , μr =
1
so
, magnetic field in free space ,
Biot-savart formula in vector form –







No comments:
Post a Comment