Organic Chemistry-HYDROCARBON
 |
HYDROCARBON |
Organic Chemistry:
- The study of organic compound ( carbon compounds ) such as hydrocarbons and their derivatives is called organic chemistry .
Organic Compounds :
- The compounds of carbon are known as organic compounds.
- Apart from carbon, most of the organic compounds contain hydrogen . many organic compounds contain oxygen or other elements too .
- e.g Methane (CH4), Ethane (C2H6), Ethene (C2H4), Ethyne (C2H2), Trichloromethane (CHCI3), Ethanol (C2H5 OH), Ethanal (CH3CHO), Ethanoic acid (CH3COOH), and Urea [CO(NH2)2].
- Exception : Though oxides of carbon (like carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide), carbonates hydrogencarbonates and carbides are also carbon compounds but they are not considered to be organic compounds. This is because their properties are very different from those of the common organic compounds.
- organic compounds are covalent compounds.
- Melting points and boiling points of Carbon compounds (or organic compounds) are low due to weak forces of attraction between their molecules.
- Most of the carbon compounds are non-conductors of electricity.
- Organic compounds occur in all living things like plants and animals.
- Initially, all the organic compounds were extracted from natural materials obtained from living things. It was, therefore, believed that the organic compounds could only be formed within a living body (plant or animal body) and hence a 'vital force' which creates in living things was necessary for their preparation.
- This vital force theory of organic compounds was disproved by a scientist Freidrich Wohler in 1828.
- Wohler prepared the organic compound 'urea' [CO(NH)2] in the laboratory from an inorganic compound 'ammonium cyanate' (NH4CNO).
 |
| Formation of urea |
- This led to the rejection of the vital force theory for the synthesis of organic compounds.
The Large Number of Organic Compounds:
- There are about more than 6 million organic compound . Many more new carbon compounds are being prepared in the laboratories every day.
- The two characteristic properties of carbon element which are responsible to form very large number of organic compounds are (i) catenation (self-linking), and (ii) tetravalency (four valency).
(i) catenation (self-linking):
- The property of carbon due to which its can join with other carbon atoms to form long carbon chains is called 'catenation.
- So, it is the property of 'catenation' of carbon element which responsible for a very large number of organic compounds .
- When carbon atoms combine with one another, three types of chains can be formed. These are : (i) straight chains, (ii) branched chains, and (iii) closed chains.
2. Tetravalency:
- Valency of carbon is 4 . so each carbon atom can form at most 4 covalent bonds with different type of atoms such as hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulphur, chlorine, and many more atoms. This leads to the formation of a large number of compounds.
Types of Organic Compounds:
- Some of the common types of organic compounds are: 1. Hydrocarbons 2. Haloalkanes 3. Aldehydes 4. Carboxylic acids 5. Alcohols 6. Ketones.
Hydrocarbons :
- A compound which consists hydrogen and carbon only is called hydrocarbon. E.g Methane (CH4), Ethane (C2H6), Ethene (C2H4), Ethyne (C2H2 ) , cyclohexane , benzene etc.
- The most important natural source of hydrocarbons is petroleum (or crude oil) and natural gas which are obtained from underground .
 |
| Hydrocarbon family |
Types of Aliphatic Hydrocarbons:
- Aliphatic Hydrocarbons are two types :
- (i) Saturated hydrocarbons and (ii) Unsaturated hydrocarbons
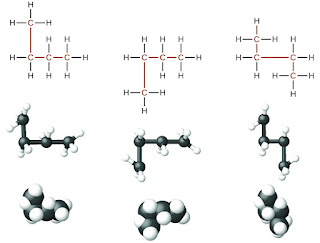
1. Saturated Hydrocarbons (Alkanes):
- A hydrocarbon in which each carbon atom consists 4 single covalent bonds is called a saturated hydrocarbon.
- i.e. In saturated Hydrocarbons each carbon atom is connected with 4 other atoms.
- Saturated hydrocarbons are also known as alkanes.
- The general formula of saturated hydrocarbons or alkanes is CnH2n+2 ,where n is the number of carbon atoms in one molecule of the alkane.
- Smallest member of Alkane family is methane (CH4) . its common name is marsh gas .
2. Unsaturated Hydrocarbons :
- A hydrocarbon in which two carbon atoms are connected by a 'double covalent bond' or a 'triple bond' is called an unsaturated hydrocarbon.
- e.g ethene (C2H4), ethyne (C2H2 ) are unsaturated hydrocarbons, because ethene contains a double bond and ethyne contains a triple bond between two carbon atoms.
- Unsaturated hydrocarbons are more reactive than saturated hydrocarbons. In other words, alkenes and alkynes are chemically more reactive than alkanes.
- The unsaturated hydrocarbons are obtained mostly from petroleum by a process called cracking.
(i)Alkenes :
- A hydrocarbon in which two carbon atoms are connected by a double covalent bonds is called an alkene.
- Thus, alkenes contain a double bond between two carbon atoms which is formed by the sharing of two electron pairs.
- The general formula of an alkene is CnH2n, where n is the number of carbon atoms in its one molecule.
- There can be no alkene having only one carbon atom.
- The simplest alkene is ethene having the molecular formula C2H4. The common name of ethene is athylen.
(ii)Alkynes:
- A hydrocarbon in which two carbon atoms are connected by a triple covalent bond is called an alkyne.
- Thus, alkyne contain a triple covalent bonds between two carbon atoms which is formed by the sharing of three electron pairs.
- There can be no alkyne having only one carbon atom.
- The general formula of alkynes is CnH2n-2 where n is the number of carbon atoms in one molecule of the alkyne.
- The simplest alkyne is ethyne having the molecular formula C2H2. The common name of ethyne is acetylène.
Alkyl Groups:
- The group formed by the removal of one hydrogen atom from an alkane molecule is called an alkyl group.
- Examples : methyl group (CH3---- ) , ethyl group (C2H5---) etc.
- Methyl group (CH3---- ) is formed by the removal of one H atom from methane (CH4); and ethyl group (C2H5---) is formed by the removal of one H atom from ethane (C2H6).
- The general formula of an alkyl group is CnH2n+1 where n is the number of carbon atoms. The alkyl groups are usually denoted by the symbol R
Cyclic Hydrocarbon :
- The hydrocarbon in which three or more carbon atoms of molecule form closed loop by covalent bond is called cyclic hydrocarbon.
- Cyclic hydrocarbons are two type:
- AliCyclic Hydrocarbon
- Aromatic Hydrocarbon
1. Saturated Cyclic Hydrocarbon :
- In saturated cyclic hydrocarbon , carbon ring of molecule consist only single covalent bonds.
- Saturated cyclic hydrocarbons are called cyclo alkane. e.g cyclo propane ( C3H6 ) , cyclo butane( C4H8 ) , cyclo pentane ( C5H10 ) , cyclo hexane ( C6H12 ) etc .
- General formula of Cyclo alkane is CnH2n . where n is number of carbon atom.
Unsaturated Cyclic Hydrocarbon:
- In unsaturated cyclic hydrocarbon, carbon ring of molecule consists at least one double or triple bond. e.g cyclo propene , cyclo butene, cyclo pentene etc.
 |
| unsaturated cyclic hydrocarbon |
2. Aromatic Compound:
- Benzene and its derivative are called aromatic compound.
- e.,g benzene ( C6H6 ) , Phenol ( C6H5OH ) , Toluene ( C6H5 CH3 ) etc.
 |
| Benzene |
- In aromatic compound , ring of molecule consists 6 carbon atoms .
- each ring consist 3 single bonds and 3 double bonds in alternate manner.
- Ring of aromatic compound is also called Benzene ring.
 |
| Aromatic Compound |
 |
| Aromatic Compound |
Related Article



No comments:
Post a Comment