What are Velocity selector and Cyclotron ? it is most important topic of NCERT in Class 12. Questions are frequently asked in the CBSE board , ICSE Board and other competitive exam ( IIT JEE, NEET, AIIMS, State Engineering exam from Velocity selector and Cyclotron .
“velocity selector and cyclotron class 12 ncert notes
“ will be very beneficial for the students who are engaged in the preparation
of upcoming board exam and competitive
exam.
In this topic,
the following terms will be illustrated.
Contents :
* What is Velocity
selector : Construction , Working
* Cyclotron: Construction
, Working
* Limitations of
cyclotron
Let Us Start :
Velocity selector and Cyclotron | Physics notes class 12
What is Velocity selector
Velocity selector is a electromagnetic device which is
used to find the charged particles of a
particular velocity from beam of charged particles having different velocity .
* The velocity selector is also called velocity filter because
it filters out particles of particular velocity.
 |
| Concept of Velocity selector |
Construction :
* It consists of two slits S1 and S2
held linearly to each other some distance apart.
* Between the slits, there is a region of uniform electric and
magnetic fields perpendicular to each other.
Working :
* Directions of the two fields are set such that they exert
forces on the charged particles in the opposite directions.
Let,
* The electric field E acts in downward direction on horizontal plane ( positive plate to negative plate ) .
* The magnetic field B acts normally into the plane of the
paper.
* Suppose a beam of positively charged particles having
different velocities enters the region of cross fields through slit S1
.
* Since the charged particles are
positive, so magnetic force Fm (= qvB ) is upward and electric force Fe (= qE ) is downward on plane .
Let velocity of particle passing through slit S2
be V .
This is happened when, there is no deviation
I.e Fe = Fm or qE =
qvB
So , v = E /
B
* Therefore, charged particles having speed v
= E/B will pass through slit S2.
* Particles with velocity other than v (= E/B ) will either be
deflected upward or downward.
* Thus velocity selector is able to select charged particles
of particular velocity out of a beam of charged particles having different
velocities.
Cyclotron
A cyclotron is a device used to accelerate heavy
charged particle to high speed.
* Cyclone is also called magnetic resonance accelerator.
* Cyclotron was discovered by Lawrence in 1932.
Construction
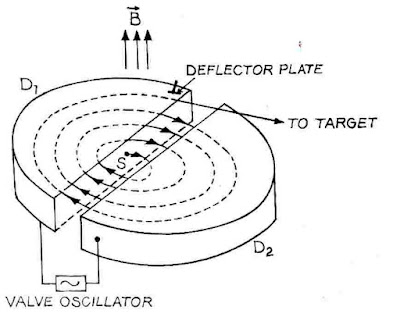 |
| Cyclotron Concept |
* It consists of two D-shaped hollow, evacuated semicircular
metal chambers D1 and D2 called dees.
* The two dees are placed horizontally with a small gap
separating them.
* An alternating potential difference of the order of 106 volt, at a frequency of 10 to 15 megacycles per second, is applied across the dees.
* Voltage alternates its polarity with the same frequency as the circular motion of the charged particle.
* The dees are enclosed in a steel box which is placed between
the poles of a strong electromagnet.
* The magnetic field of about 1.6 tesla is perpendicular to the plane of the dees.
* An ion source is located at the centre S in the gap between the dees. It consists of a small chamber containing a heated filament and a gas such as hydrogen (for protons) or deuterium (for deuterons).
* The ions come out through a small hole in the ion source and are available to be accelerated.
* An intense magnetic field B of about 1.6 tesla is set up perpendicular to the plane of dees by a large electromagnet.
* The whole space inside the dees is evacuated to a pressure
of about 10-3 mm of mercury.
Working
* The positive ion
(e.g. proton, α-particle, etc.) is injected with a small velocity from an
ion source S near the centre of the device.
* Inside the dee, the ion simply follows a circutar path in
the perpendicular magnetic field. It is because electric field inside the
metallic dees is zero.
* It moves in a semicircle in one of the dee and enter into
other dee through air gap between them .
* When ions passes through gap between two dees then ion is accelerated by the electric field
across the gap and gains kinetic energy qV .
* Every half revolution potenial dtifference between the dees
has been reversed .
* Due to gain in kinetic energy , radius of circular path increases in every
half cycle .
* Eventually, the ion orbit becomes equal to the size of the
machine. At this point, an electrostatic field provided by a high- voltage electrode
deflects the ion out of the magnetic field and towards a target.
* In a typical cyclotron, an ion may make 50 to 100
revolutions.
Parameter in Cyclotron :
* Radius of path
r = mv / qB
* Time period
T = 2πm / qB = Constant
* Cyclotron Frequency
f = qB / 2πm
* Angular Frequency
ω =
qB / m
* Maximum Kinetic
energy
Kmax
= mv02 / 2
(where , v0
= maximum velocity in last half circular
motion )
Kmax = B2q2r20
/ 2m
( Where , r0
= radius of last half circular motion )
* Number of completed turns,
N = Kmax / 2qV
Limitations of cyclotron
* One of the
assumptions in the design of a cyclotron is that the frequency of revolution of
the ion circulating in the magnetic field is independent of its speed. This is
true only for speeds that are much less than the speed of light.
* At higher speeds, the mass of the ion will increase according
to Einstein's formula .It means that the ion will take a longer time to
complete the semicircular path in the dee than the time for half-cycle of
alternating voltage. As a result, the ion starts lagging behind the electric
field and is eventually lost by collision against the walls of the dees.
* One way to deal with the increase in mass with speed is to
increase the magnitude of magnetic field (B) as the ion speeds up. Such a
device is called synchrotron.
(ii) Cyclotron is suitable only for accelerating heavy
particles such as protons, α-particles, etc.
It is not suitable for accelerating electrons. It is
because the mass of electron is very small and hence gains speed quickly due to
small increase in energy.
(iii) Cyclotron cannot accelerate uncharged particles
(e.g., neutrons).
(iv) For very high kinetic energy (e.g. 500GeV), it is
impossible to design magnetic field system.

No comments:
Post a Comment