 |
| Dispersion of light through prism and scattering : Light notes class X cbse board |
GLASS PRISM
 |
| triangular glass prism |
* The triangular glass prism is a transparent object made of glass having two triangular faces and three rectangular faces. The opposite faces of a triangular glass prism are not parallel to one another. They are inclined at an angle to one another. The angle between its opposite refracting faces is called the angle of the prism.
* Triangular glass prism' is usually called 'glass prism' and sometimes even just 'prism'.
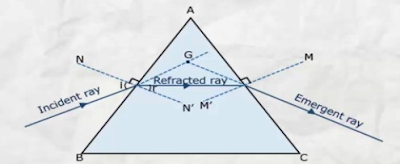 |
| The emergent ray of light in a glass prism is not parallel to the incident ray of light |
because the opposite faces of the glass prism are not parallel to one another. In refraction through glass prism, the emergent ray is deviated from its original direction by a certain angle. And we say that light rays get deviated on passing through a glass prism.
REFRACTION OF LIGHT THROUGH A GLASS PRISM
When a ray of light passes through a glass prism, refraction of light occurs at both opposite surfaces of prism ,when it enters the prism as well as when it leaves the prism.
* Since the refracting surfaces (PQ and PR) of the prism are not parallel, therefore, the emergent ray and incident ray are not parallel to one another.
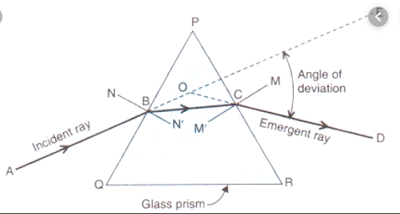 |
| REFRACTION OF LIGHT THROUGH A GLASS PRISM |
* A ray of light AB is incident on the face PQ of the prism. The incident ray AB is going from air (rarer medium) into glass (denser medium), so it bends towards the normal NBN' and the direction BC inside the glass prism. Thus, BC is the refracted ray of light which bends towards the base QR of the prism.
* When the ray of light BC travelling in the glass prism comes out into air at point C, refraction takes place again. Since the ray BC is going from glass (denser medium) into air (rarer medium), so it bends away from the normal MCM' and goes along the direction CD in the form of emergent ray. The emergent ray of light CD bends towards the base QR of the prism.
* Thus when a ray of light passes through a prism, it bends towards the base of prism. In other words, when a ray of light passes through a prism, it bends towards the thicker part of the prism.
* The emergent ray CD is not parallel to the incident ray AB. There has been a deviation (or change) in the path of light in passing through the prism.
* The angle between incident ray line and emergent ray line is called angle of deviation.
White light:
Any light that gives spectrum similar to that of sunlight is called white light.
DISPERSION OF LIGHT:
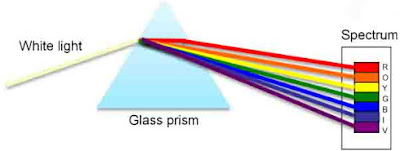
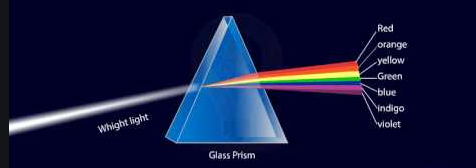
* In the year 1665, Newton found that if a beam of white light is passed through a triangular glass prism, the white light splits to form a band of seven colours on a white screen. The band of seven colours formed on a white screen is called spectrum of white light and this phenomenon is called dispersion of light.
 |
| dispersion of light |
* The seven colours of the spectrum are: Red, Orange, Yellow, Green, Blue, Indigo, and Violet. The seven colours of the spectrum can be denoted by the word VIBGYOR where V stands for Violet, I for Indigo, B for Blue, G for Green, Y for Yellow, O for Orange and R for Red.
Explaination:
* White light is a mixture of lights of seven colours : red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo and violet. The dispersion of white light occurs because different colours of white light travel at different speeds through the glass prism. The amount of refraction depends on the speed of coloured light in glass.
* When white light consisting of seven colours falls on a glass prism, each colour in it is refracted (or deviated) by a different angle, with the result that seven colours are spread out to form a spectrum.
* The red colour has the maximum speed in glass prism, so the red colour is deviated the least. Due to this the red colour forms the upper part of the spectrum.
* On the other hand , the violet colour has the minimum speed in glass prism, so the violet colour is deviated the maximum. Due to this violet colour appears at the bottom of the spectrum.
Re-Combination of Spectrum Colours to Give White Light
* White light can be dispersed into its seven constituent colours. Newton showed that the seven coloured lights of the spectrum can be recombined to give back white light.
This can be done as follows
* A triangular glass prism PQR is placed on its base QR and another similar prism P'Q'R' is placed in reversed position on its vertex P'. When a beam of white light is allowed to fall on the first prism PQR, then white light is obtained on a screen S placed behind the second prism P'Q'R'.
Newton explained these observations as follows.
 |
| Re-Combination of Spectrum Colours to Give White Light |
* The first glass prism PQR disperses (splits) the white light into seven coloured rays. The second glass prism P'Q'R' receives all the seven coloured rays from the first prism and recombines them into original white beam of light which falls on the screen S.
* The recombination of seven colours, produced by first prism, is due to the fact that the second prism has been placed in reversed position due to which the refraction produced by the second prism is equal and opposite to that produced by the first prism.
Rainbow:
 |
| rainbow |
* The rainbow is an arch of seven colours visible in the sky which is produced by the dispersion of sun's light by raindrops in the atmosphere. The rainbow is actually a natural spectrum of sunlight in the sky.
* The raindrops in the atmosphere act like many small prisms. As white sunlight enters and leaves these raindrops (or water drops), the various coloured rays present in white light are refracted by different amounts due to which an arch of seven colours called rainbow is formed in the sky.
* The rainbow is formed in the sky when the sun is shining and it is raining at the same time. A rainbow is always formed in a direction opposite to that of the sun. Due to this We can see the rainbow if we stand with our back towards the sun and rain in fronf of us.
Explaination: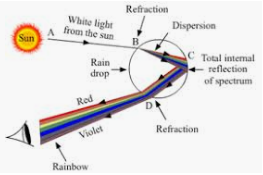 |
| Formation of rainbow |
* A ray of white sunlight AB enters the raindrop at point B and undergoes refraction and dispersion to form a spectrum. This spectrum undergoes total internal reflection at point C within the raindrop and finally refracted out of the raindrop at point D .
* This spéctrum produced by the raindrops in the atmosphere is seen from the earth. The red colour of spectrum appears at the top of the rainbow whereas violet colour appears at its bottom.
* The formation of seven-coloured rainbow in the sky shows that white sunlight consists of a mixture of seven coloured lights.
* We can also see a rainbow on a sunny day if we look through a spray of water from a fountain (or through a waterfall) with the sun behind us. Before we go further and discuss atmospheric refraction, please answer the following questions :
SCATTERING OF LIGHT
* Scattering of light means to throw light in various random directions. Light is scattered when it falls on various types of suspended particles in its path.
 |
| Scattering of light |
* The earth's atmosphere is a heterogeneous mixture of minute particles. These particles include suspended particles of dust, tiny water droplets and molecules of air. The Cólour of Scattered Light Depends on the Size of Scattering Particles.
(1) The larger particles of dust and water droplets present in the atmosphere scatter the light as such due to which the scattered light also appears white.
Dust particles and water droplets suspended in the atmosphere are much larger than the wavelength range of visible light. When white light coming from the sun hits these larger particles, it gets reflected or scattered in different directions. The different colours of white light are reflected by the dust and water particles in the same way. Due to this, the scattered light appears white (because it still contains all the colours of white light).
Dust particles and water droplets suspended in the atmosphere are much larger than the wavelength range of visible light. When white light coming from the sun hits these larger particles, it gets reflected or scattered in different directions. The different colours of white light are reflected by the dust and water particles in the same way. Due to this, the scattered light appears white (because it still contains all the colours of white light).
* Thus, when white sunlight falls on larger particles (like dust particles and water droplets) present in the atmosphere, it is scattered as such, so the scattered light also appears white.
(ii) The extremely minute particles such as the air molecules present in the atmosphere scatter mainly the blue light present in the white sunlight.
The air molecules (nitrogen and oxygen gas molecules) present in the atmosphere are smaller than the wavelength range of visible light. So, when light coming from the sun hits these air molecules, it behaves differently. Since the different colours of white light have different wavelengths, so they are affected differently.
The air molecules (nitrogen and oxygen gas molecules) present in the atmosphere are smaller than the wavelength range of visible light. So, when light coming from the sun hits these air molecules, it behaves differently. Since the different colours of white light have different wavelengths, so they are affected differently.
* The lower wavelength lights (blues) are scattered much more by the air molecules but the higher wavelength lights (reds) are scattered much less.
* Thus, when white sunlight falls on the extremely small particles like air molecules present in the atmosphere, it is not scattered as white light. The molecules of air scatter mainly the lower wavelengths of light which have blue shades.
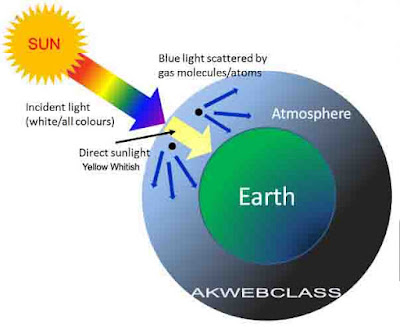
Why the Sky is Blue
The scattering of blue component of the white sunlight by air molecules present in the atmosphere causes the blue colour of the sky.
This can be explained as follows.
* The sunlight is made up of seven coloured lights mixed together. When sunlight passes through the atmosphere, most of the longer wavelength lights (such as red, orange, yellow, etc.) present in it do not get scattered much by the air molecules and hence pass straight through.
* The shorter wavelength blue light is scattered all around the sky by air molecules in the atmosphere. Whichever direction we look, some of this scattered blue light enters our eyes. Since we see the blue light from everywhere overhead, the sky looks blue.
* Only a little of the blue light present in white sunlight is scattered by the atmosphere which makes the sky appear blue. Most of the blue light remains behind unscattered due to which the composition of sunlight remains almost unaltered.Because of this the direct sunlight coming through the blue sky still appears to be white.
* In outer space, the sky looks dark and black instead of blue. This is because there is no atmosphere containing air in the outer space to scatter sunlight. Since there is no scattered light to reach our eyes in outer space, therefore, the sky looks dark and black there. This is why the astronauts who go to outer space find the sky to be dark and black instead of blue.
'Danger' signal lights are red in colour. Why ?
This is because the red coloured light having longer wavelength is the least scattered by fog or smoke particles. Due to this the red light can be seen in the same colour even from a distance.
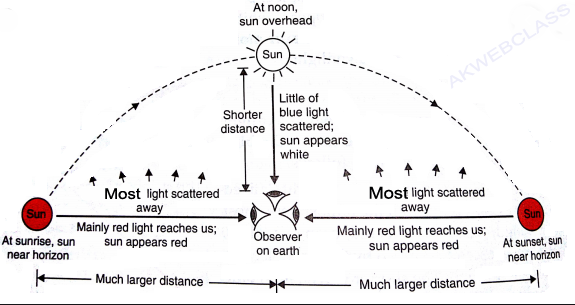
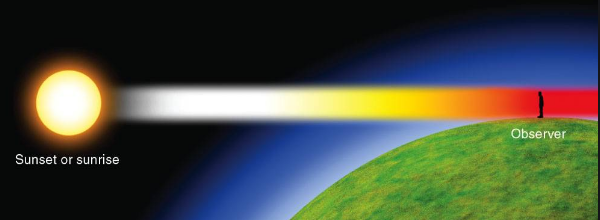
Why the Sun Appears Red at Sunrise and Sunset
The sun and the surrounding sky appear red at sunrise and at sunset because at that time most of the blue colour present in sunlight has been scattered out and away from our line of sight, leaving behind mainly red colour in the direct sunlight beam that reaches our eyes.
This can be explained as follows.
At the time of sunrise and sunset when the sun is near the horizon, the sunlight has to travel the greatest distance through the atmosphere to reach us.
 |
| Sun Appears Red |
* During this long journey of sunlight, most of the shorter wavelength blue-colour present in it is scattered out and away from our line of sight.
* So, the light reaching us directly from the rising sun or setting sun consists mainly of longer wavelength red colour due to which the sun appears red .
* Due to the same reason, the sky surrounding the rising sun and setting sun also appears red. Thus, at sunrise and sunset, the sun itself as well as the surrounding sky appear red.
Why the sun appears white when it is overhead in the sky?
* When the sun is overhead (as at noon), then the light coming from the sun has to travel a relatively shorter distance through the atmosphere to reach us. During this shorter journey of sunlight, only a little of the blue colour of the white light is scattered (most of the blue light remains in it).
* Since the light coming from the overhead sun has almost all its component colours in the right proportion, therefore, the sun in the sky overhead appears white to us .
Tyndall Effect :
* The scattering of light by particles in its path is called Tyndall effect.
* When a beam of sunlight enters a dusty room through a window, then its path becomes visible to us. This is because the tiny dust particles present in the air of room scatter the beam of light all around the room. And when this scattered light enters our eyes, we can see the beam of light.
* Tyndall effect can also be observed when sunlight passes through the canopy of a dense forest. Here, tiny water droplets in the mist scatter sunlight.
* The wavelength of blue light is almost half that of the red light.
* The blue light present in sunlight is scattered 10 times more than the red light.
Related Article ( Click to read )

No comments:
Post a Comment